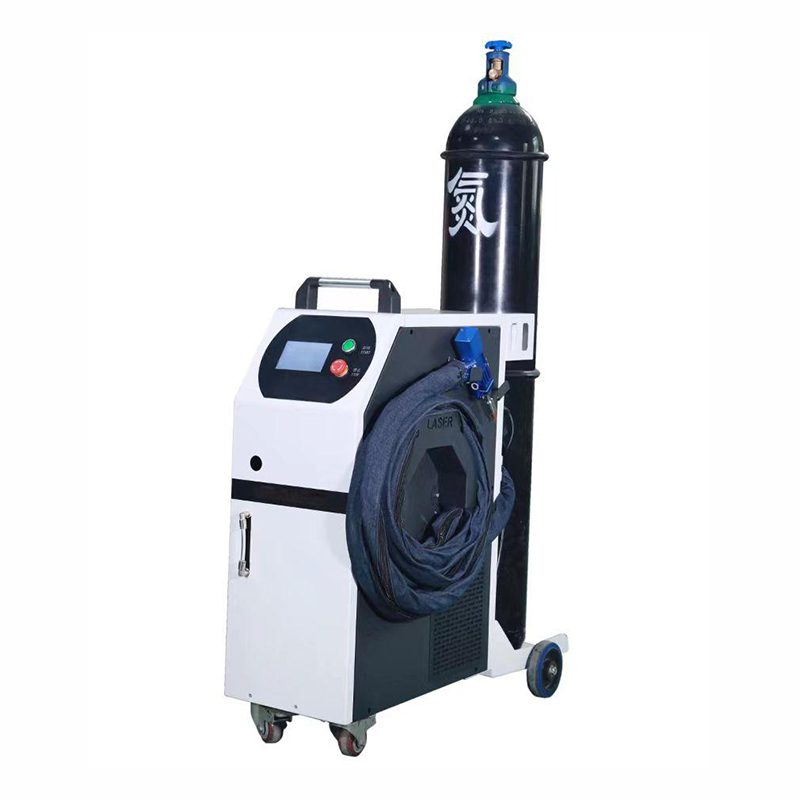
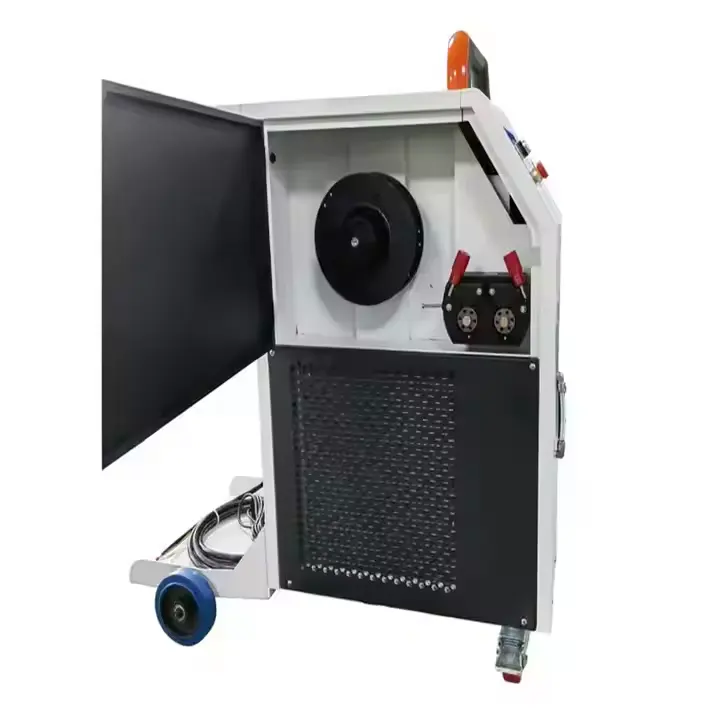
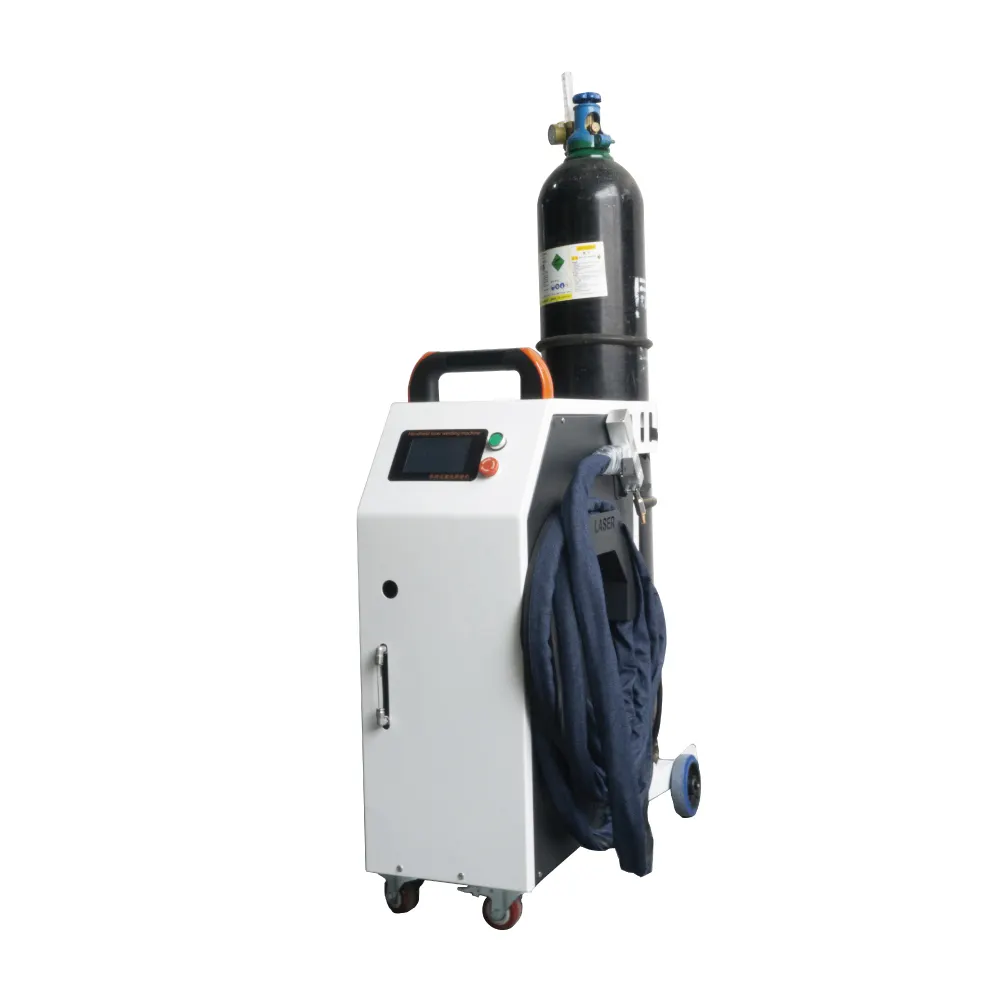
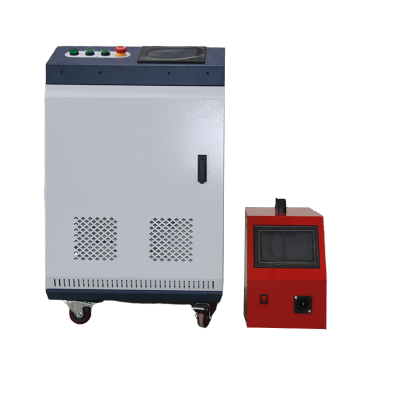
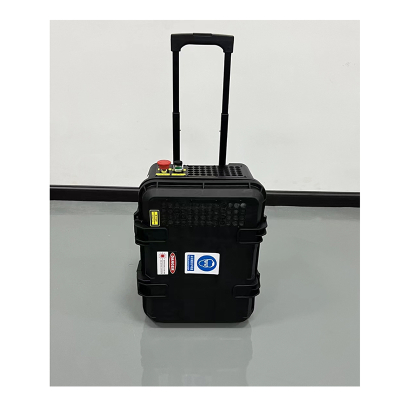
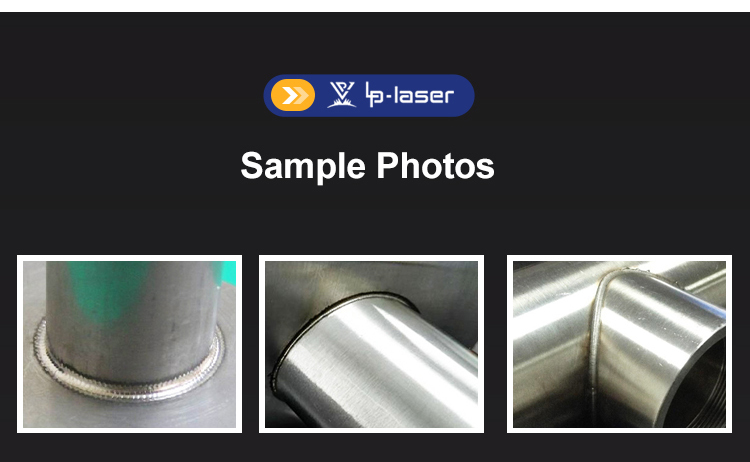
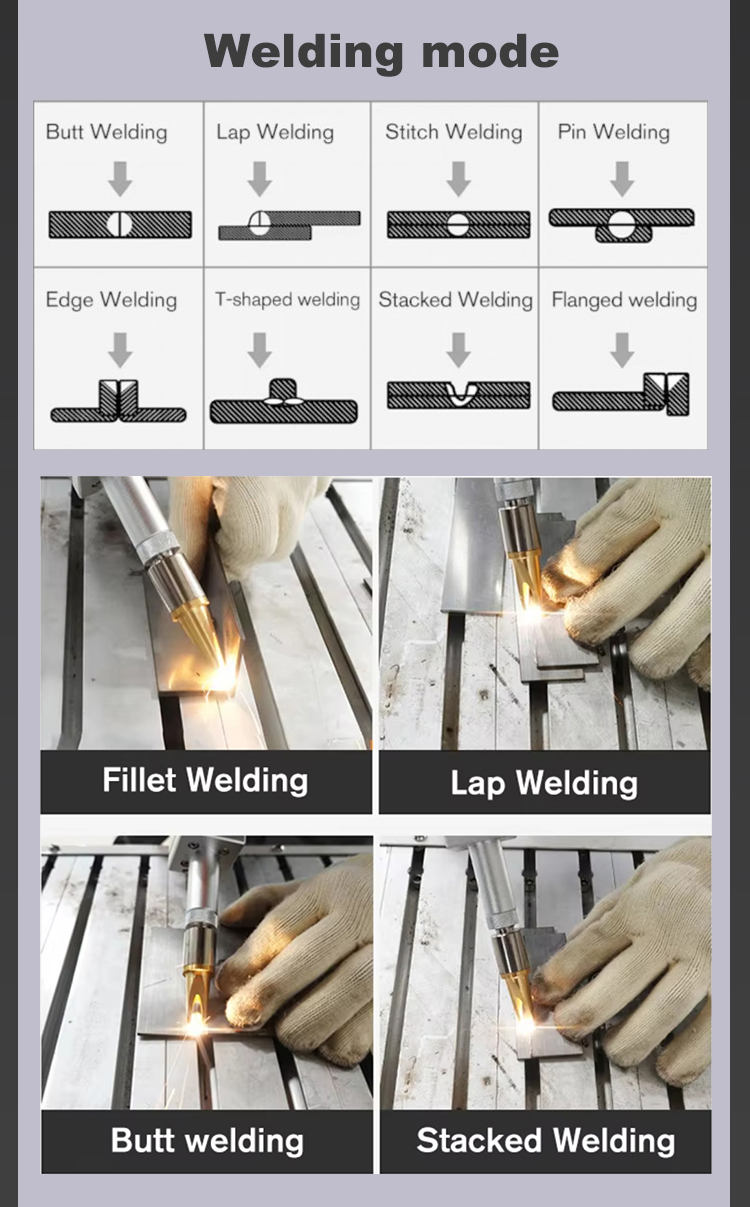
High Performance Metal Laser Welding Machine
Exceptional Precision
Metal laser welding machines are renowned for their extraordinary precision. The laser beam can be focused to an incredibly small spot size, often in the range of a few tens of microns. This high level of precision empowers operators to create minute and highly accurate welds. In industries such as jewelry making, where intricate designs and delicate metalwork are the norm, or in electronics manufacturing, where the smallest components need to be joined with utmost accuracy, these machines shine. The small focused spot ensures that the heat input is concentrated precisely on the welding area. This minimizes the heat - affected zone (HAZ), reducing the risk of distortion or damage to the surrounding material and guaranteeing high - quality welds with excellent joint integrity.
High - Speed Welding
Compared to many traditional welding methods, like arc welding or gas - tungsten arc welding (GTAW), metal laser welding machines offer significantly faster welding speeds. The high - energy density of the laser beam enables rapid melting of the metal. In industrial production settings, this increased speed can lead to a substantial boost in productivity. For example, in a large - scale metal fabrication factory, the use of a metal laser welding machine can drastically cut down the time required to weld multiple components. This not only results in faster turnaround times but also increases the overall output, making it a cost - effective solution for high - volume production.
Versatile Material Compatibility
These machines exhibit remarkable versatility when it comes to material compatibility. They can effectively weld a wide spectrum of metal materials. Common metals such as stainless steel, carbon steel, aluminum, and copper are easily joined. Additionally, they can handle more exotic alloys like titanium and nickel - based alloys. What's more, metal laser welding machines have the capability to weld dissimilar metals, a challenging task with traditional welding techniques. This versatility makes them invaluable in industries such as aerospace, where different metals are used in the construction of aircraft components to balance strength, weight, and other performance characteristics.
Compact and Portable Design (in some models)
Some metal laser welding machines are designed with a compact and portable structure. Unlike large, stationary traditional welding systems, these portable models are lightweight and feature an ergonomic welding head. This allows operators to carry and maneuver the machine easily, reaching difficult - to - access areas. For industries such as on - site construction, where welding needs to be done in various locations, or automotive repair shops that may require welding in tight spaces, the portability of these machines is a game - changer.
Low Heat - Affected Zone
The concentrated nature of the laser beam in metal laser welding machines results in a minimal heat - affected zone. This is a crucial advantage, particularly when working with materials that are sensitive to heat or when maintaining the integrity of the base metal is of utmost importance. In applications such as the manufacturing of precision machinery, where dimensional accuracy is critical, the small HAZ ensures that the surrounding areas of the weld remain unaffected. This reduces the need for post - welding machining or corrective measures and helps to preserve the mechanical properties of the metal, such as hardness and toughness, in the vicinity of the weld.
Cost - Effective Operation in the Long Run
Despite their advanced technology, metal laser welding machines offer cost - effective operation over time. They generally have relatively low energy consumption compared to some traditional welding equipment, leading to reduced utility bills. Moreover, they often require fewer consumables. In many cases, there is no need for continuous wire feeding or large amounts of shielding gas, further cutting down on operational costs. The reduced need for post - welding finishing, such as grinding and polishing to smooth out rough welds, also saves time and labor costs. Additionally, the durability and reliability of these machines contribute to lower maintenance costs over their lifespan, making them an attractive option for businesses aiming to optimize their welding processes and reduce overall production costs.
User - Friendly Operation
Most metal laser welding machines are designed with user - friendliness in mind. They typically come with intuitive control panels or interfaces. Operators can easily adjust parameters such as laser power, pulse duration, and welding speed according to the specific requirements of the job. Even those with limited welding experience can quickly learn to use the machine effectively after a short training period. The design of the welding head often focuses on ergonomics, ensuring comfortable handling during extended use and reducing operator fatigue. Some models are also equipped with built - in safety features, such as protective shields and interlocks, to prevent accidental exposure to the laser beam, enhancing both usability and safety.
Metal Laser Welding Machine Introduction
In the fast - paced world of metalworking and manufacturing, the metal laser welding machine has emerged as a revolutionary tool, reshaping the landscape of metal joining processes. This state - of - the - art equipment combines the power of laser technology with advanced engineering to offer unparalleled precision, efficiency, and versatility, catering to a diverse range of industries.
Working Principle
At its essence, the metal laser welding machine operates on the principle of laser - induced melting and fusion. A high - intensity laser beam, typically generated by a fiber - optic - based laser source, lies at the heart of its functionality. This laser beam is then transmitted through a flexible optical fiber to the welding head, which serves as the operator - controlled interface.
When the operator initiates the welding process, the laser beam is directed onto the metal surfaces intended for joining. The highly concentrated energy of the laser beam is swiftly absorbed by the metal. As a result, the metal atoms start to vibrate vigorously. This intense vibration generates substantial heat, rapidly elevating the temperature of the metal to its melting point. Consequently, a molten pool is formed at the weld site.
As the laser beam progresses along the joint, the molten metal flows together. Once the laser beam moves away, the molten metal cools and solidifies, creating a robust and durable weld. Some advanced models of metal laser welding machines offer the option to control the laser pulse. This feature provides even more precise control over the welding process, especially when dealing with delicate metals or complex joint geometries. By adjusting parameters such as pulse duration, frequency, and energy, operators can fine - tune the heat input, ensuring optimal welding results.
| Laser Type | Fiber Laser |
| Laser Power | 1500W/2000W/3000W |
| Laser Wavelength | 1080±10nm |
| Output Power Tunability | 10-100% |
| Cooling Way | Air Cooling |
| Fiber Length | Standard 15m or Specify |
| Working Method | CW/Pulse Mode |
| Speed Range | 0~120 mm |
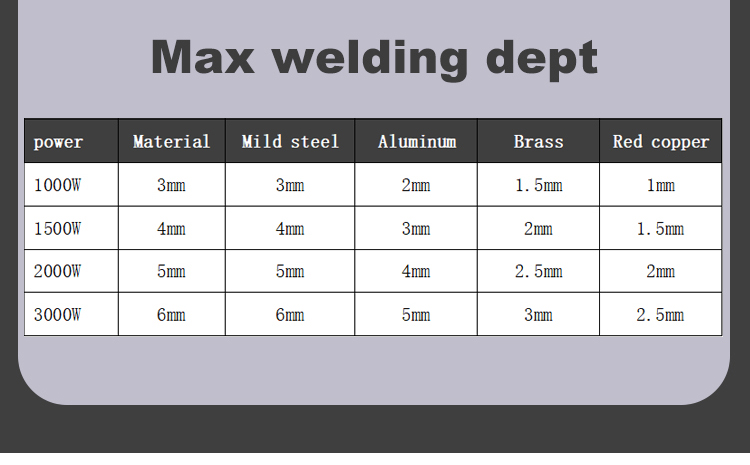
| Welding Thickness | 0.5~5mm |
Q6: WHAT IS THE LASER’S WAVELENGTH, AND WHY DOES IT MATTER?
A6: OUR MACHINE USES A 1064 NM ND:YAG LASER, WHICH IS OPTIMAL FOR HARD MATERIALS.
Q7: HOW DOES IT HANDLE CURVED OR IRREGULAR SURFACES?
A7: THE ROBOTIC ARM OR 6-AXIS SYSTEM ENSURES EVEN CLEANING ON COMPLEX GEOMETRIES.
Q8: IS IT SAFE TO USE ON HISTORICAL ARTIFACTS?
A8: YES, PULSE MODE MINIMIZES THERMAL DAMAGE, MAKING IT IDEAL FOR MUSEUMS.
Q9: WHAT IS THE DUTY CYCLE OF THE LASER SYSTEM?
A9: CONTINUOUS OPERATION UP TO 8 HOURS WITH PROPER COOLING.
Q10: CAN IT REMOVE PAINT FROM DELICATE SURFACES LIKE WOOD?
A10: YES, BUT PULSE MODE MUST BE USED TO AVOID DAMAGE.